Taking root cuttings from plants is a method of vegetative propagation that allows you to propagate new plants from existing ones. Here is a general procedure to take root cuttings from a plant:
1. Choose the Plant and Timing: Select a plant that is known to propagate well from root cuttings. It’s best to take root cuttings during the plant’s dormant season, typically in late winter or early spring before new growth begins.
2. Prepare the Tools and Materials: Gather the necessary tools and materials, including a sharp, clean knife or pruners, a clean cutting board or surface, a pot or container with well-draining soil or rooting medium, and optional rooting hormone (available at garden centers).
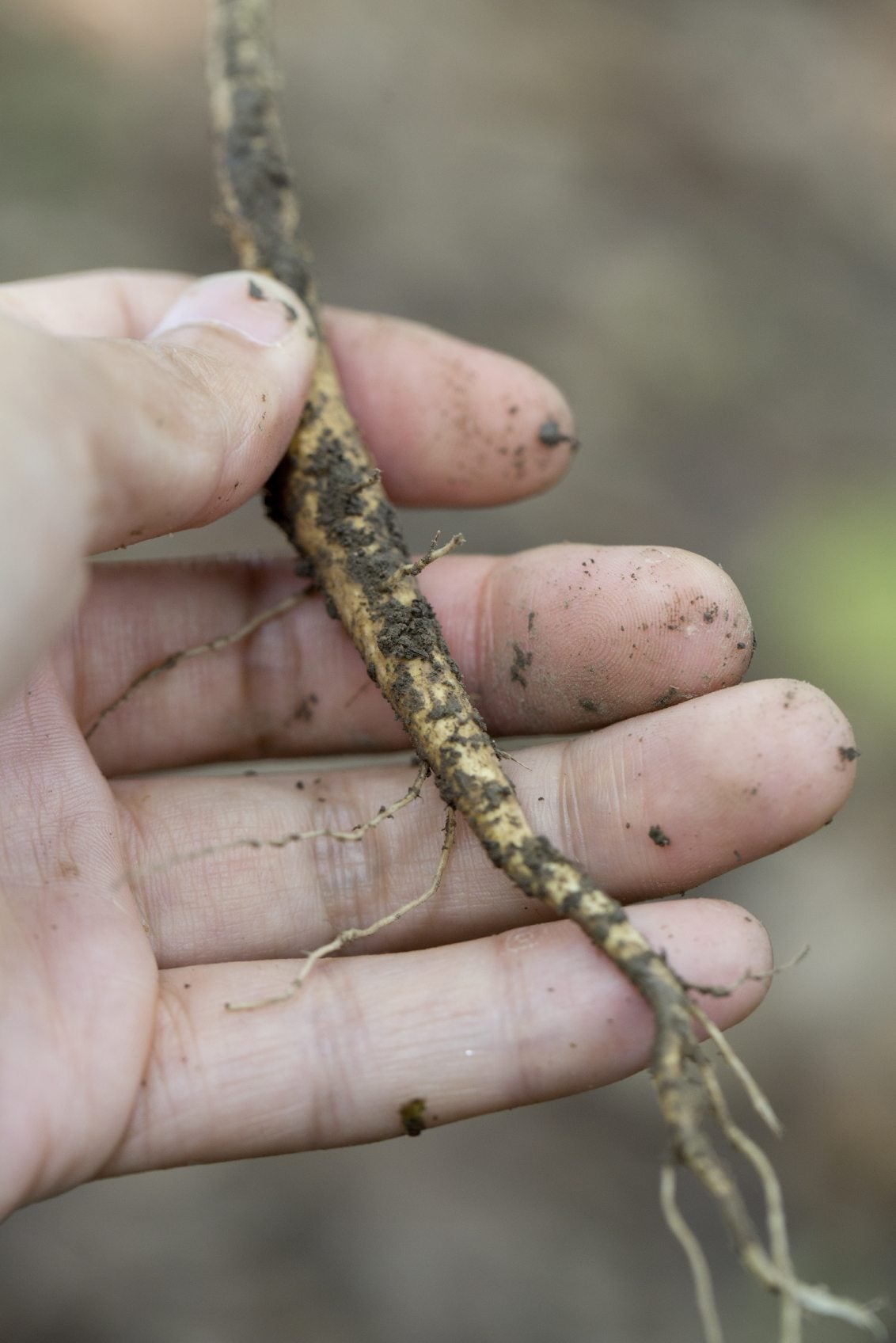
3. Prepare the Parent Plant: Dig around the base of the parent plant and carefully expose the roots. Choose healthy, thick, and vigorous roots for the best chances of successful propagation. Avoid using thin or damaged roots.
4. Take Root Cuttings: Cut sections of the roots with a sharp knife or pruners. Aim for cuttings that are 2 to 6 inches (5-15 cm) long, depending on the plant species and its root structure. Each cutting should have at least one bud or growing point.
5. Treat the Cuttings (Optional): Some plants benefit from using a rooting hormone to stimulate root development. Dip the cut end of each root cutting into the rooting hormone powder or solution, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
6. Prepare the Growing Medium: Fill a pot or container with a well-draining soil mix or rooting medium. Moisten the medium to ensure it is evenly damp but not waterlogged.
7. Insert the Cuttings: Make holes in the growing medium using a pencil or your finger, spacing them appropriately based on the plant’s requirements. Insert the root cuttings into the holes, burying them to the appropriate depth, leaving the bud or growing point above the soil.
8. Provide Care: Place the container in a suitable location with filtered light and maintain a consistent temperature and humidity. Water the cuttings gently to keep the medium slightly moist but not soggy. Avoid overwatering, as excessive moisture can lead to rot.
9. Monitor and Wait: Regularly check the cuttings for signs of new growth, indicating successful root development. This process can take several weeks to months, depending on the plant species.
10. Transplanting: Once the cuttings have developed a healthy root system and new growth, they can be transplanted into individual pots or directly into the desired planting site, following the specific requirements of the plant species.
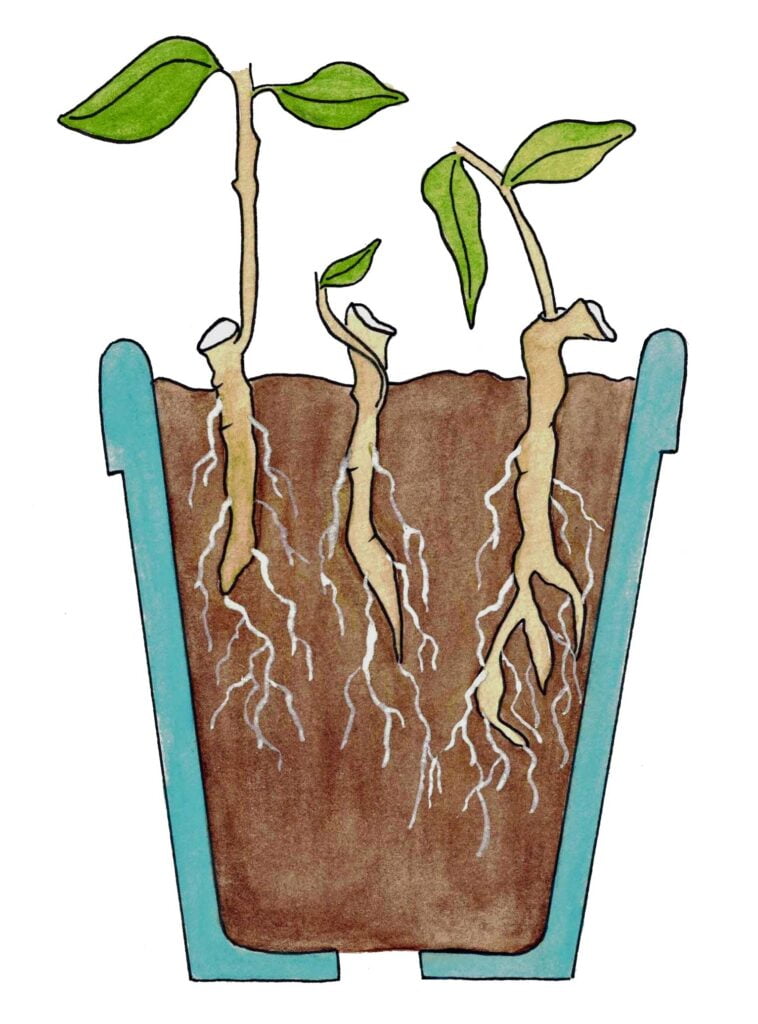
It’s important to note that not all plant species can be propagated successfully from root cuttings. Some plants are more suitable for other propagation methods like stem cuttings or division. Additionally, it’s always recommended to research and follow specific instructions for the particular plant you are working with, as propagation methods can vary depending on the species.
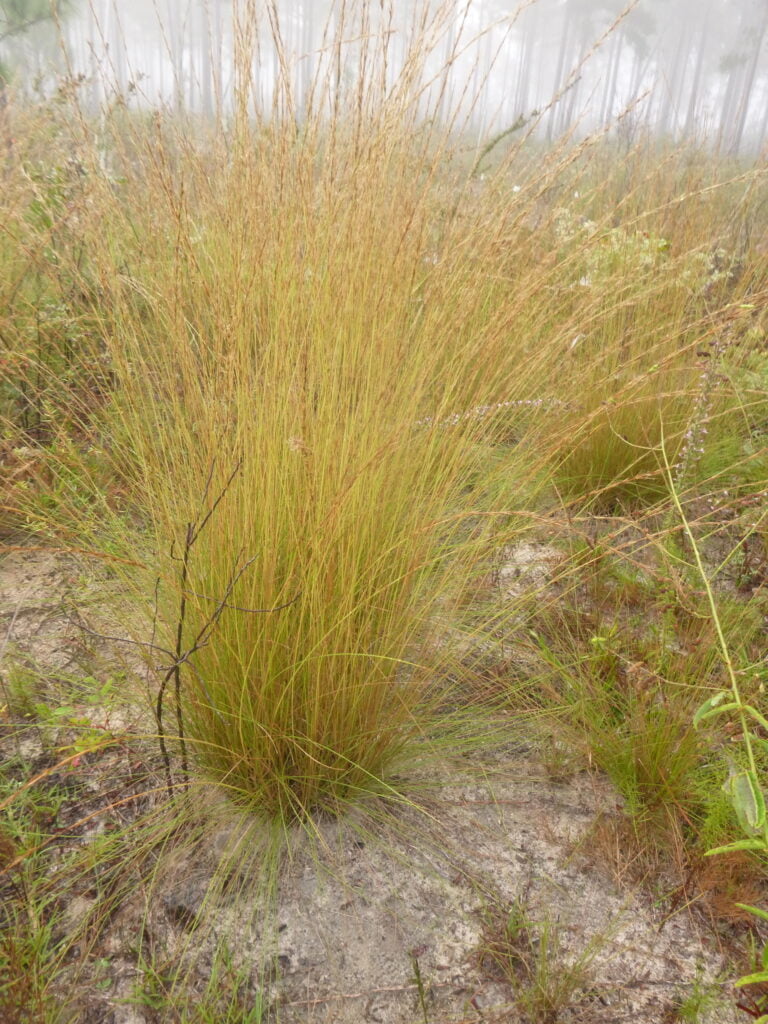

Install Southern Wiregrass (Aristida beyrichiana) at Your Site
Longleaf Pine, American Turkey Oak, and Wiregrass (Aristida beyrichiana) are three of the most important staples in Central Florida’s xeric upland scrub and sandhill habitats. Have Three Psilos, Inc. install Wiregrass at your site.

